Yellowfin Tuna Species Guide and Yellowtail Tuna

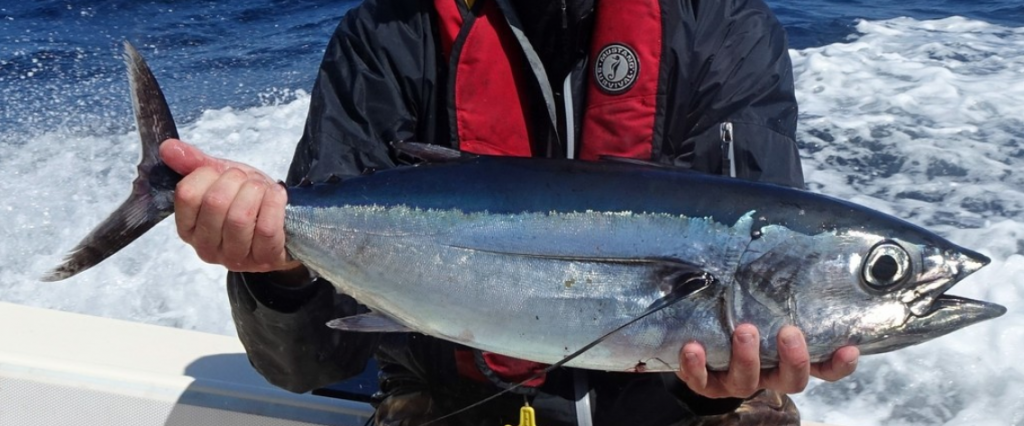
Yellowfin Tuna (also known as Thunnus albacares or “Ahi” in Hawaiia) is a species of tuna that is deep blue on top with a shallow yellow line in the middle of their body going to the tail. Their fins are also yellowish in color. Yellowfin is one of the larger tuna species and very tasty.
Yellowfin tuna have the potential of reaching up to a weight of 400lbs or 180kg. They are mainly found in the warmer offshore waters such as Gulf of Meixco, Hawaii, Caribbean, Eastern and Western Pacific.
Yellowfin tuna group together in enormous schools and can be seen feeding as they break the surface chasing after bait. Like other Tuna species they eat a large number of different bait fish like sardines and mackerel, squid, and even small pelagic crabs.
Yellowfin tuna are strong fighters. Like all tuna they pull hard for their size, and as mentioned above, they can get quite large. They almost never jump when hooked, instead swim in large circles making it a long process to get them in the boat. They are a great gamefish and a pleasure to catch. As a bonus, they are also great to eat.
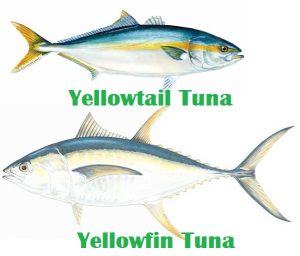
Difference between Yellowfin and Yellowtail Tuna
Yellowfin tuna and Yellowtail tuna are both species of fish that belong to the same family, Scombridae, but they are different species. Yellowfin tuna (Thunnus albacares) is a species of tuna that is found in the open waters of the tropical and subtropical oceans worldwide, while yellowtail tuna (Thunnus albacares) is a species of tuna that is found primarily in the waters off the coast of Japan and Australia.
Yellowfin tuna is a large fish that can grow up to 6.5 feet in length and weigh up to 440 pounds. It has a metallic blue-black back and upper sides with a silver belly and bright longer yellow fins. Yellowtail tuna, on the other hand, is a medium-sized fish that can grow up to 6 feet in length and weigh up to 110 pounds. It has a dark blue back and upper sides with a silver belly and smaller yellow fins. The two species can be distinguished by the size, color, and location of the yellow fins. Yellowfin tuna has yellow fins that are located at the top of its body and are longer, while yellowtail tuna has yellow fins that are located at the bottom of its body and are smaller.
Yellowfin tuna is considered to have a stronger flavor and firmer texture than yellowtail tuna. Yellowfin tuna is often used for sashimi and sushi, while yellowtail tuna is often grilled or served as sashimi. Yellowtail tuna is considered to be a good choice for grilling or cooking because of its milder flavor and softer texture. It is also considered to be a good choice for raw fish dishes because of its softer texture and milder flavor.
Specific details on How to Catch Yellowfin Tuna
Check out other species of tuna.


 Penn Tuna Fishing Rod & Reel Combo
Penn Tuna Fishing Rod & Reel Combo Fishing Pliers and Knife Combo
Fishing Pliers and Knife Combo View Best Tuna Fishing Lures
View Best Tuna Fishing Lures